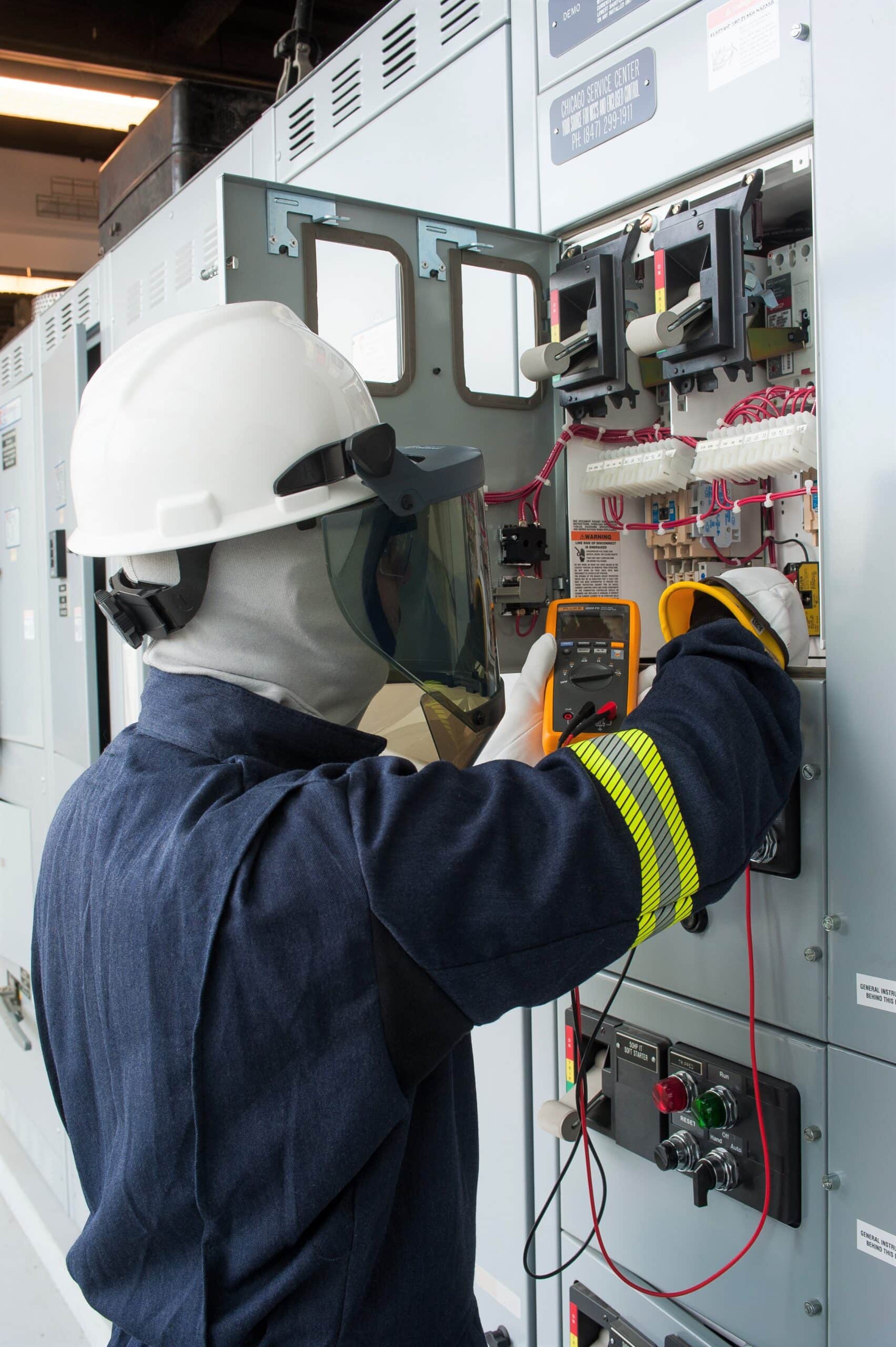
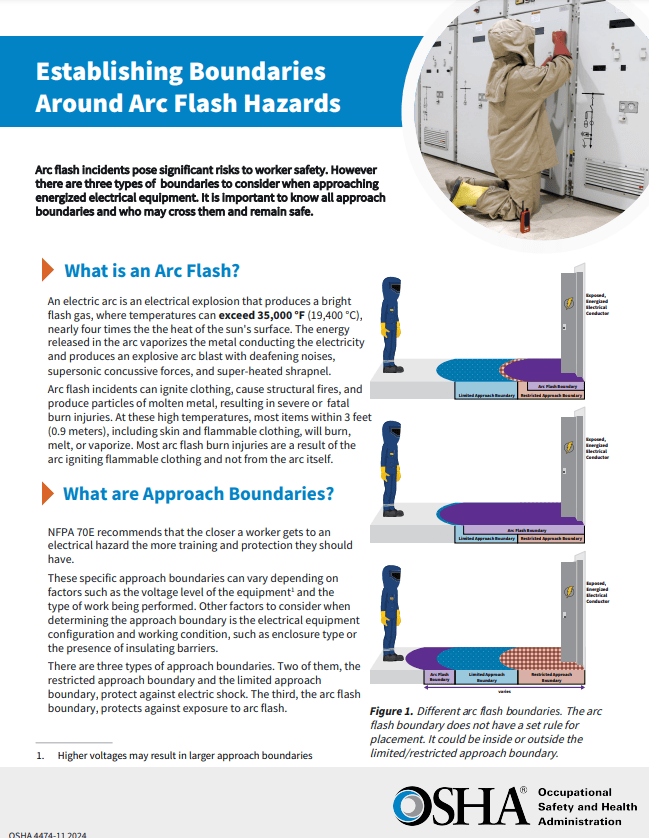
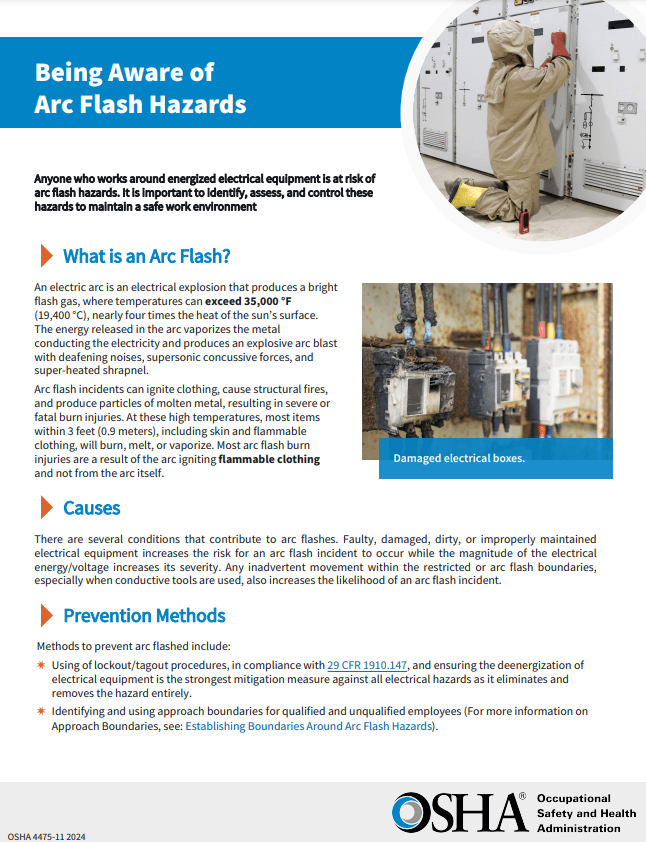
In November 2024, OSHA released new guidance on arc flash safety for the first time in almost 20 years. The guidance is specific to NFPA 70E in protecting commercial, industrial and residential electricians from arc flash hazards. It does not pertain to electrical utility transmission and distribution. The guidance focuses on several important topic areas but primarily targets the underutilization of appropriate arc-rated clothing and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Arc flash incidents remain one of the most hazardous risks for electrical workers, potentially causing severe injuries or fatalities. OSHA’s recent updates to arc flash safety guidelines aim to address these dangers more effectively, incorporating the latest research and technological advancements in personal protective equipment (PPE) and safety protocols. These updates build on the principles established by NFPA 70E, offering clearer, actionable instructions for electrical safety. This blog delves into the specifics of the updated guidance and the impact it will have on electrical workers’ safety.
Key Updates in the 2024 Guidance
Enhanced PPE Standards
OSHA now emphasizes the importance of arc-rated PPE to withstand extreme temperatures of an arc flash, often exceeding 35,000°F. Specific changes include:
- Improved classification of arc rated clothing based on incident energy levels.
- Mandates for undergarments that resist ignition, addressing the dangers of flammable clothing beneath PPE.
- Expanded use of advanced materials like lightweight, durable flame-resistant fabrics to enhance worker comfort and compliance.
Updated Risk Assessments
Revised guidelines require a more comprehensive arc flash risk assessment, including:
- Precise calculations of incident energy at every work point (not just at a single panel).
- Evaluation of shock protection boundaries to reflect current understanding of electrical hazards.
- Enhanced labeling protocols for better identification of hazard zones and PPE requirements.
- Proactive Safety Measures
In addition, OSHA now prioritizes creating an electrically safe work condition before any task begins, aligning with NFPA 70E Article 110. Changes include:
- Strict lockout/tagout procedures with real-time verification of de-energization.
- Incorporation of stored energy hazard assessments into routine checks.
- Emergency response planning to ensure readiness during arc flash events.
Implications for Electrical Workers and Employers
The revised guidance will significantly improve workplace safety by reducing the risk of arc flash injuries through better preparation and prevention. Employers must ensure their teams are thoroughly trained in the new requirements and provide updated PPE aligned with the latest standards. Workers will benefit from enhanced protection and a clearer understanding of hazard zones and risk mitigation practices.
Although compliance may initially require investments in new PPE and training programs, the long-term benefits—including fewer accidents, lower medical costs, and improved worker confidence—far outweigh the costs. Employers who implement these changes proactively position themselves as safety leaders in their industries.
For more information on the updated guidance on electric arc flash, visit OSHA’s website at https://www.osha.gov/electrical/flash-hazards